In-depth Explanation of Yala: Building a Modular DeFi Yield Aggregator with $YU Stablecoin as a Medium
Bitcoin was originally designed as a peer-to-peer electronic payment system. However, over a decade of development, it has increasingly been viewed as “digital gold,” serving as a “mascot” for value storage rather than a payment method. With the emergence of DeFi, inscriptions, and additional Layer 2 solutions, new opportunities for expanding Bitcoin’s value and ecosystem have opened up in recent years.
More and more development teams are working to build a true DeFi ecosystem for Bitcoin, fully unlocking its liquidity potential. Yala shares this vision, aiming to combine Bitcoin’s security and decentralization with a modular protocol framework, using the $YU stablecoin as a medium of exchange and store of value. This allows Yala to connect Bitcoin seamlessly with other ecosystems, enabling holders to earn yield from various DeFi protocols.
This article will comprehensively analyze Yala’s protocol design, $YU stablecoin, tokenomics, ecosystem development, team background, and funding, helping users better understand and participate in the project.
What is Yala?
Yala aims to position itself as the DeFi infrastructure for Bitcoin. Creating a thriving and open ecosystem seeks to enhance Bitcoin’s liquidity while offering users smooth access to decentralized financial services, products, and opportunities across different networks, allowing them to benefit from the decentralized finance space.

Source: Yala
To achieve this goal, Yala is building a modular infrastructure that allows for deploying cross-chain modules across various ecosystems, including Ethereum-compatible chains like EVM and non-EVM chains like Solana. This will enhance Bitcoin’s composability across different ecosystems. The core components of the Yala protocol include the over-collateralized stablecoin $YU, the cross-chain protocol MetaMint, and the gateway Yala Bridge, among others. Yala adopts a dual-token system, with $YU (a Bitcoin-backed yield-bearing stablecoin) and $YALA (the governance token of the Yala ecosystem) at its core.
In mid-October, Yala announced the launch of its testnet. Users can deposit BTC and MetaMint $YU, manage positions, and stake $YU to earn reward points called $BERRIES. According to the official announcement, earning $BERRIES increases a user’s recognition within the Yala ecosystem and can provide potential rewards, including future airdrops.
Team Background and Funding
Yala was founded in 2023, and its team members have extensive experience in the blockchain and DeFi sectors. They come from leading organizations both within and outside the industry, such as Alchemy Pay, Binance Labs, Circle, MakerDAO, Lido, Microsoft, and Capital One. Kaitai Chang, the co-founder and COO of Yala, previously worked at Binance and APX Finance.
On October 10 of this year, Yala announced the completion of a $8 million seed funding round led by Ethereal Ventures and Polychain, with participation from Galaxy Digital, Amber Group, HashKey Capital, ABCDE Capital, Anagram, UTXO Management, and others. According to the team, the funds will primarily be used for team expansion, product development, enhancing security, and preparing for the mainnet launch.
Yala Protocol Architecture
Yala adopts a modular design that spans several layers, including consensus, data availability, and execution. Its architecture is mainly composed of three interconnected components:
- Yala Bridge: The function of this gateway is to allow users to deposit BTC and convert it into yBTC, a tokenized representation of Bitcoin on the Yala platform. This tokenized BTC can then be used as collateral within the Yala ecosystem.

Source: Yala
- Yala Network: After receiving yBTC, users can leverage it to mint the stablecoin $YU across different blockchains. They can then participate in various DeFi protocols, including staking, lending, and other functions.
- Professional Mode: Yala plans to launch two versions of its platform: a simplified version for regular users and a professional version for advanced users. In the professional mode, users can seamlessly access Layer 2 (L2) solutions like Babylon, Ethena, and Lorenzo protocols using yBTC, enabling them to earn additional yield through token staking while maintaining exposure to Bitcoin.
An important innovation within this protocol framework is MetaMint, a groundbreaking solution that integrates both Yala Bridge and Yala Network. By eliminating the need for users to interact directly with wrapped assets, MetaMint significantly simplifies the cross-chain process, making it easier for users to navigate between ecosystems.

Source: Yala
With the support of the MetaMint cross-chain protocol, users can easily mint the stablecoin $YU on the target chain by simply depositing BTC. The process is simple and intuitive, offering a highly user-friendly experience.
Additionally, MetaMint introduces a multi-functional collateral method that supports multiple assets for minting $YU on the target chain. In addition to native BTC, wrapped BTC on EVM chains are also accepted as collateral. This enhances the liquidity of $YU and Bitcoin, creating a more stable and efficient market environment.
$YU Stablecoin Mechanism
The stablecoin $YU plays an extremely important role in the entire Yala ecosystem, functioning both as an asset and a tool.
In summary, $YU is a Bitcoin-collateralized stablecoin with a soft peg to the US dollar. This allows Bitcoin holders to participate in DeFi activities without selling their BTC. Compared to other stablecoins on the market, $YU has improved its scalability, yield generation, and fee structure.
Multi-Chain and Multi-Protocol Compatibility
Unlike stablecoins focusing solely on a single blockchain, $YU is compatible with multiple blockchains, including Ethereum-based EVM chains and non-EVM chains like Solana, to fully enhance asset liquidity. Furthermore, $YU supports integrating various DeFi protocols across different networks, such as staking, lending, and more, to foster its scalability and broad adoption.
Dual Profit Model for $YU Holders and the Platform
Many stablecoins heavily rely on centralized infrastructure and third-party custodians, who retain all profits, such as trading fees or interest from stablecoin reserves, while holders of the stablecoin cannot earn yield. In the Yala protocol, the system-generated fees are borne by $YU holders. The platform charges fees for creating and maintaining the vaults to ensure long-term, stable profits. As for the $YU holders, they can earn income through various decentralized finance activities.
Stability Mechanisms for $YU
For a stablecoin, maintaining a stable value is crucial. To ensure this stability, the Yala team employs several mechanisms: over-collateralization, stability fees, liquidation mechanisms, and incentivized operators. These methods continuously monitor collateral and valuation levels, adjusting risk parameters to manage volatility and maintain the peg. The specifics are as follows:
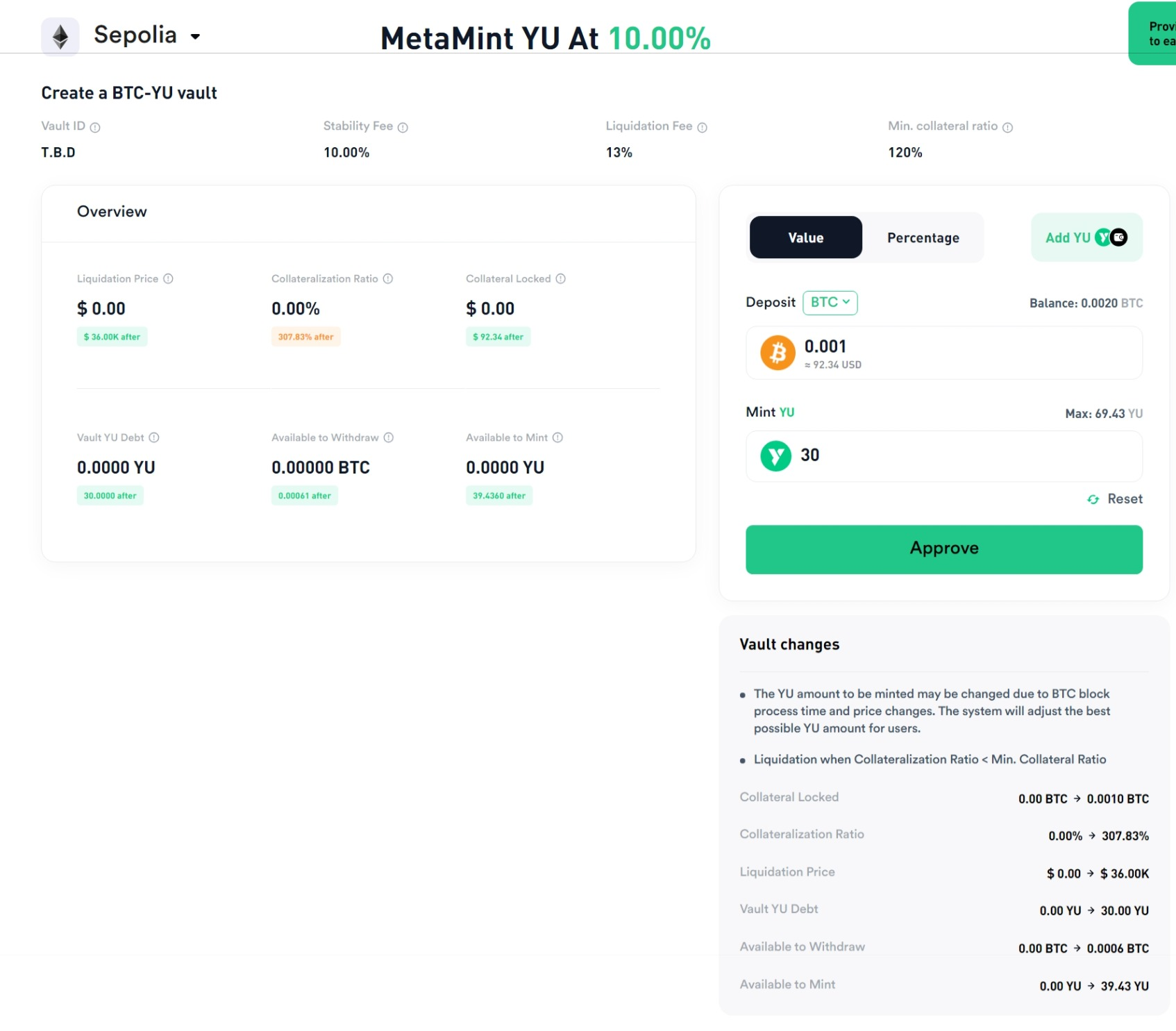
Over-Collateralization
Over-collateralization ensures that the value of collateral, such as Bitcoin, always exceeds the value of the issued $YU stablecoin.
Source: Yala
In Yala’s current testnet, the collateralization ratio for BTC is set at a minimum of 120%.
Stability Fee
The stability fee helps manage the overall supply and demand levels of $YU. It is charged as a percentage of the $YU debt in each vault. When $YU falls below its peg, the stability fee increases, making it more expensive for users to hold $YU debt, which may encourage them to repay their debt and reduce the supply of $YU, thus driving up its price. Conversely, if $YU is above its peg, the stability fee decreases.
Liquidation Mechanism
Yala’s liquidation system consists of an automatic liquidation mechanism and incentivized participants known as Keepers. When the value of the collateral falls below a predefined threshold (the liquidation ratio), the system will auction the collateral to repay the $YU debt. The auction mechanism is well-structured, and the team has primarily drawn inspiration from MakerDAO’s Dog and Clipper contracts.
Incentivized Market Operations
$YU encourages market makers, arbitrageurs, and other participants to help manage and maintain the value of $YU through activities such as trading and arbitrage.
In addition to the core mechanisms mentioned above, Yala Savings Rate (YSR) and other features influence the supply and demand balance of the $YU stablecoin. YSR is a savings contract within the Yala protocol, similar to MakerDAO’s Dai Savings Rate (DSR), designed to incentivize users to deposit and hold $YU by offering stable returns. The activation of YSR helps reduce market sell pressure on $YU. The yield generated by YSR comes from fees and revenue generated by the Yala vaults.
Yala Tokenomics
In Yala’s tokenomics model, the ecosystem’s governance token, $YALA, plays a crucial role in addition to the stablecoin $ YU
.
The $YALA token has not yet been issued, and key details such as its supply and distribution model have not yet been disclosed. However, earlier this year, the team provided a detailed explanation of its role.
In the Yala ecosystem, the $YALA token serves both governance and utility functions, as outlined below:
Governance Function
Decentralization and community governance have always been core principles for the Yala team. $YALA holders can vote on important decisions, such as adding new collateral types and modifying related risk parameters.
Utility Token Function
- Fee Payments: Users can use $YALA to pay for fees associated with accessing and using the Yala SDK, as well as transaction fees for platform node operators and other services within the ecosystem.
- Capital Restructuring: Similar to MakerDAO’s Flopper and Flapper mechanisms, in cases of insufficient collateral backing for the stablecoin, $YALA tokens can be minted and sold to replenish system capital. This ensures that the platform maintains its solvency at all times.
In addition to these core functions, the team also mentioned a burn mechanism. When there is an excess of $YALA tokens in circulation, the surplus tokens will be repurchased and burned, which will help increase their value and maintain balance in the token economy.
In addition to these two tokens, the team has also introduced $BERRIES as reward points on the running testnet. According to the team, $BERRIES represents a user’s participation and activity level within the Yala ecosystem. The more $BERRIES a user accumulates, the higher their rank on the leaderboard, and the more potential rewards they can earn, including future airdrops.

Source: Yala
Users can earn $BERRIES points by completing various tasks on the testnet, such as interacting with the platform, engaging in social media activities, daily check-ins, and submitting product feedback. Additionally, users can invite friends via referral links to participate and earn points, and form teams with friends to join in lucky draw events.
Ecosystem Development and Future Outlook
Recent data shows that over 332,000 users have joined the testnet, with approximately 171,000 BTC staked. Regarding community development, Yala has around 81,700 followers on its official X (formerly Twitter) account, 34,300 users in its Telegram group, and 37,500 users on Discord.
Beyond product development, Yala seeks external partnerships to foster connections between Bitcoin and broader ecosystems. Key partners include Babylon, Botanix, Nubit, Polyhedra, and Avail. Moving forward, the team will focus on R&D for both the testnet and mainnet, with plans to gradually launch the $YU stablecoin, an insurance module, and a governance framework.
Conclusion
Yala’s goal is to address the liquidity gap in the current Bitcoin ecosystem and build a modular DeFi yield aggregator for Bitcoin. With the Yala solution, BTC holders can seamlessly participate in decentralized financial products and services across various blockchain networks, earning yield natively.
While certain design ideas draw inspiration from MakerDAO, Yala’s MetaMint cross-chain protocol brings innovation by eliminating the intermediate wrapping step, simplifying user interaction with DeFi protocols. Overall, there is much anticipation for the further refinement of the Yala product and its development after the mainnet launch.
In-depth Explanation of Yala: Building a Modular DeFi Yield Aggregator with $YU Stablecoin as a Medium
What is Yala?
Team Background and Funding
Yala Protocol Architecture
$YU Stablecoin Mechanism
Yala Tokenomics
Ecosystem Development and Future Outlook
Conclusion
Bitcoin was originally designed as a peer-to-peer electronic payment system. However, over a decade of development, it has increasingly been viewed as “digital gold,” serving as a “mascot” for value storage rather than a payment method. With the emergence of DeFi, inscriptions, and additional Layer 2 solutions, new opportunities for expanding Bitcoin’s value and ecosystem have opened up in recent years.
More and more development teams are working to build a true DeFi ecosystem for Bitcoin, fully unlocking its liquidity potential. Yala shares this vision, aiming to combine Bitcoin’s security and decentralization with a modular protocol framework, using the $YU stablecoin as a medium of exchange and store of value. This allows Yala to connect Bitcoin seamlessly with other ecosystems, enabling holders to earn yield from various DeFi protocols.
This article will comprehensively analyze Yala’s protocol design, $YU stablecoin, tokenomics, ecosystem development, team background, and funding, helping users better understand and participate in the project.
What is Yala?
Yala aims to position itself as the DeFi infrastructure for Bitcoin. Creating a thriving and open ecosystem seeks to enhance Bitcoin’s liquidity while offering users smooth access to decentralized financial services, products, and opportunities across different networks, allowing them to benefit from the decentralized finance space.

Source: Yala
To achieve this goal, Yala is building a modular infrastructure that allows for deploying cross-chain modules across various ecosystems, including Ethereum-compatible chains like EVM and non-EVM chains like Solana. This will enhance Bitcoin’s composability across different ecosystems. The core components of the Yala protocol include the over-collateralized stablecoin $YU, the cross-chain protocol MetaMint, and the gateway Yala Bridge, among others. Yala adopts a dual-token system, with $YU (a Bitcoin-backed yield-bearing stablecoin) and $YALA (the governance token of the Yala ecosystem) at its core.
In mid-October, Yala announced the launch of its testnet. Users can deposit BTC and MetaMint $YU, manage positions, and stake $YU to earn reward points called $BERRIES. According to the official announcement, earning $BERRIES increases a user’s recognition within the Yala ecosystem and can provide potential rewards, including future airdrops.
Team Background and Funding
Yala was founded in 2023, and its team members have extensive experience in the blockchain and DeFi sectors. They come from leading organizations both within and outside the industry, such as Alchemy Pay, Binance Labs, Circle, MakerDAO, Lido, Microsoft, and Capital One. Kaitai Chang, the co-founder and COO of Yala, previously worked at Binance and APX Finance.
On October 10 of this year, Yala announced the completion of a $8 million seed funding round led by Ethereal Ventures and Polychain, with participation from Galaxy Digital, Amber Group, HashKey Capital, ABCDE Capital, Anagram, UTXO Management, and others. According to the team, the funds will primarily be used for team expansion, product development, enhancing security, and preparing for the mainnet launch.
Yala Protocol Architecture
Yala adopts a modular design that spans several layers, including consensus, data availability, and execution. Its architecture is mainly composed of three interconnected components:
- Yala Bridge: The function of this gateway is to allow users to deposit BTC and convert it into yBTC, a tokenized representation of Bitcoin on the Yala platform. This tokenized BTC can then be used as collateral within the Yala ecosystem.

Source: Yala
- Yala Network: After receiving yBTC, users can leverage it to mint the stablecoin $YU across different blockchains. They can then participate in various DeFi protocols, including staking, lending, and other functions.
- Professional Mode: Yala plans to launch two versions of its platform: a simplified version for regular users and a professional version for advanced users. In the professional mode, users can seamlessly access Layer 2 (L2) solutions like Babylon, Ethena, and Lorenzo protocols using yBTC, enabling them to earn additional yield through token staking while maintaining exposure to Bitcoin.
An important innovation within this protocol framework is MetaMint, a groundbreaking solution that integrates both Yala Bridge and Yala Network. By eliminating the need for users to interact directly with wrapped assets, MetaMint significantly simplifies the cross-chain process, making it easier for users to navigate between ecosystems.

Source: Yala
With the support of the MetaMint cross-chain protocol, users can easily mint the stablecoin $YU on the target chain by simply depositing BTC. The process is simple and intuitive, offering a highly user-friendly experience.
Additionally, MetaMint introduces a multi-functional collateral method that supports multiple assets for minting $YU on the target chain. In addition to native BTC, wrapped BTC on EVM chains are also accepted as collateral. This enhances the liquidity of $YU and Bitcoin, creating a more stable and efficient market environment.
$YU Stablecoin Mechanism
The stablecoin $YU plays an extremely important role in the entire Yala ecosystem, functioning both as an asset and a tool.
In summary, $YU is a Bitcoin-collateralized stablecoin with a soft peg to the US dollar. This allows Bitcoin holders to participate in DeFi activities without selling their BTC. Compared to other stablecoins on the market, $YU has improved its scalability, yield generation, and fee structure.
Multi-Chain and Multi-Protocol Compatibility
Unlike stablecoins focusing solely on a single blockchain, $YU is compatible with multiple blockchains, including Ethereum-based EVM chains and non-EVM chains like Solana, to fully enhance asset liquidity. Furthermore, $YU supports integrating various DeFi protocols across different networks, such as staking, lending, and more, to foster its scalability and broad adoption.
Dual Profit Model for $YU Holders and the Platform
Many stablecoins heavily rely on centralized infrastructure and third-party custodians, who retain all profits, such as trading fees or interest from stablecoin reserves, while holders of the stablecoin cannot earn yield. In the Yala protocol, the system-generated fees are borne by $YU holders. The platform charges fees for creating and maintaining the vaults to ensure long-term, stable profits. As for the $YU holders, they can earn income through various decentralized finance activities.
Stability Mechanisms for $YU
For a stablecoin, maintaining a stable value is crucial. To ensure this stability, the Yala team employs several mechanisms: over-collateralization, stability fees, liquidation mechanisms, and incentivized operators. These methods continuously monitor collateral and valuation levels, adjusting risk parameters to manage volatility and maintain the peg. The specifics are as follows:
Over-Collateralization
Over-collateralization ensures that the value of collateral, such as Bitcoin, always exceeds the value of the issued $YU stablecoin.

Source: Yala
In Yala’s current testnet, the collateralization ratio for BTC is set at a minimum of 120%.
Stability Fee
The stability fee helps manage the overall supply and demand levels of $YU. It is charged as a percentage of the $YU debt in each vault. When $YU falls below its peg, the stability fee increases, making it more expensive for users to hold $YU debt, which may encourage them to repay their debt and reduce the supply of $YU, thus driving up its price. Conversely, if $YU is above its peg, the stability fee decreases.
Liquidation Mechanism
Yala’s liquidation system consists of an automatic liquidation mechanism and incentivized participants known as Keepers. When the value of the collateral falls below a predefined threshold (the liquidation ratio), the system will auction the collateral to repay the $YU debt. The auction mechanism is well-structured, and the team has primarily drawn inspiration from MakerDAO’s Dog and Clipper contracts.
Incentivized Market Operations
$YU encourages market makers, arbitrageurs, and other participants to help manage and maintain the value of $YU through activities such as trading and arbitrage.
In addition to the core mechanisms mentioned above, Yala Savings Rate (YSR) and other features influence the supply and demand balance of the $YU stablecoin. YSR is a savings contract within the Yala protocol, similar to MakerDAO’s Dai Savings Rate (DSR), designed to incentivize users to deposit and hold $YU by offering stable returns. The activation of YSR helps reduce market sell pressure on $YU. The yield generated by YSR comes from fees and revenue generated by the Yala vaults.
Yala Tokenomics
In Yala’s tokenomics model, the ecosystem’s governance token, $YALA, plays a crucial role in addition to the stablecoin $ YU
.
The $YALA token has not yet been issued, and key details such as its supply and distribution model have not yet been disclosed. However, earlier this year, the team provided a detailed explanation of its role.
In the Yala ecosystem, the $YALA token serves both governance and utility functions, as outlined below:
Governance Function
Decentralization and community governance have always been core principles for the Yala team. $YALA holders can vote on important decisions, such as adding new collateral types and modifying related risk parameters.
Utility Token Function
- Fee Payments: Users can use $YALA to pay for fees associated with accessing and using the Yala SDK, as well as transaction fees for platform node operators and other services within the ecosystem.
- Capital Restructuring: Similar to MakerDAO’s Flopper and Flapper mechanisms, in cases of insufficient collateral backing for the stablecoin, $YALA tokens can be minted and sold to replenish system capital. This ensures that the platform maintains its solvency at all times.
In addition to these core functions, the team also mentioned a burn mechanism. When there is an excess of $YALA tokens in circulation, the surplus tokens will be repurchased and burned, which will help increase their value and maintain balance in the token economy.
In addition to these two tokens, the team has also introduced $BERRIES as reward points on the running testnet. According to the team, $BERRIES represents a user’s participation and activity level within the Yala ecosystem. The more $BERRIES a user accumulates, the higher their rank on the leaderboard, and the more potential rewards they can earn, including future airdrops.

Source: Yala
Users can earn $BERRIES points by completing various tasks on the testnet, such as interacting with the platform, engaging in social media activities, daily check-ins, and submitting product feedback. Additionally, users can invite friends via referral links to participate and earn points, and form teams with friends to join in lucky draw events.
Ecosystem Development and Future Outlook
Recent data shows that over 332,000 users have joined the testnet, with approximately 171,000 BTC staked. Regarding community development, Yala has around 81,700 followers on its official X (formerly Twitter) account, 34,300 users in its Telegram group, and 37,500 users on Discord.
Beyond product development, Yala seeks external partnerships to foster connections between Bitcoin and broader ecosystems. Key partners include Babylon, Botanix, Nubit, Polyhedra, and Avail. Moving forward, the team will focus on R&D for both the testnet and mainnet, with plans to gradually launch the $YU stablecoin, an insurance module, and a governance framework.
Conclusion
Yala’s goal is to address the liquidity gap in the current Bitcoin ecosystem and build a modular DeFi yield aggregator for Bitcoin. With the Yala solution, BTC holders can seamlessly participate in decentralized financial products and services across various blockchain networks, earning yield natively.
While certain design ideas draw inspiration from MakerDAO, Yala’s MetaMint cross-chain protocol brings innovation by eliminating the intermediate wrapping step, simplifying user interaction with DeFi protocols. Overall, there is much anticipation for the further refinement of the Yala product and its development after the mainnet launch.



